WhitePaper
- Home
- / WhitePaper
- Introduction & Philosophy
- Accounts and Transactions
- Messages and Contracts
- Applications
- Token Model
- Consensus and Governance
- Technical Chain Specs
- Validator Design
- Tokenomics
- Team
- Future Directions
- Conclusion
- Download WhitePaper
LibraChain
Where Balance Meets Liberty
1. Introduction & Philosophy
LibraChain is a next-generation, gasless Layer 1 blockchain built on a fork of Ethereum’s Dencun upgrade and enhanced with mesh networking technology for superior scalability and resilience. Its architecture has been purpose- engineered to remove the biggest barriers to Web3 adoption: gas complexity, onboarding friction, and limited interoperability.
By introducing a dual-token model
- GAS : a non-tradeable, zero-value technical token with infinite supply, minted dynamically per block to abstract away gas costs from users.
- LIB : the native governance and utility token, enabling ecosystem participation, staking, and protocol-level decision-making
LibraChain allows users to interact with decentralized applications without holding any tokens beforehand , creating a Web2-like user experience while preserving the decentralization, security, and composability that define blockchain technology.
Validator onboarding is streamlined through one-click setup , reducing the technical barrier for network participation and promoting a healthy, globally distributed validator set. Adaptive block gas limits and the efficiency benefits of Dencun’s EIP-4844 blob transactions provide the throughput and cost efficiency required for large-scale adoption.
LibraChain’s omnichain interoperability framework ensures frictionless asset and data movement across leading Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks, positioning it as a central hub for cross-chain DeFi, gaming, RWA tokenization, and enterprise blockchain applications
In short, LibraChain combines the proven stability of Ethereum’s architecture with innovations in gas abstraction, scalability, and interoperability , paving the way for mass Web3 adoption at both consumer and enterprise levels.
2. Accounts and Transactions
Gasless Execution with Internal GAS Balances
Unlike Ethereum, where EOAs must hold ETH to cover gas fees, LibraChain introduces an internal GAS token system for fee abstraction:
- GAS is a technical token with zero market value, infinite supply , and non-tradable .
- Users are never required to manage or hold GAS manually.
- Each transaction is automatically topped up with GAS from a system- level minting contract that allocates gas dynamically to the sender.
- This allows zero-balance wallets to participate fully in on-chain activity without preloading funds.
In Ethereum, the need to pay upfront gas fees poses onboarding friction — especially for new users unfamiliar with wallets, seed phrases, or exchange flows
In contrast, LibraChain accounts are designed with usability-first principles : GAS token system for fee abstraction:
- New users can receive assets, interact with DApps, and even deploy contracts without ever needing to understand gas .
- The GAS system acts as a permissionless sponsor layer , invisibly funding the user’s experience under the hood
- Developers can build on-chain apps that require no setup or token holding from the user — ideal for mobile-first or consumer-grade applications.
Smart Contract and Storage
Contract accounts in LibraChain behave identically to Ethereum’s, with full support for:
- Solidity and Vype
- Persistent storage
- Message calls, contract creation, self-destruction
- EVM-compatible opcodes and gas metering (for internal accounting, not user-facing)
Contracts can observe , but not manipulate, the GAS abstraction layer — ensuring separation of concerns and resistance to exploitation.
3. Messages and Contracts
In LibraChain, the execution model builds directly on Ethereum’s architecture but extends it through gas abstraction and EIP-4844 blob integration.
LibraChain supports two core interaction types: transactions and messages. Both are mechanisms for transferring value, invoking contracts, or triggering computations, but differ in origin and processing context.
Transactions
A transaction in LibraChain is a signed data package originating from an externally owned account (EOA) . It is broadcasted to the network and includes the following fields:
- Recipient Address – the destination of the call (EOA or contract)
- Signature – proving the sender’s authority
- Value – the amount of LIB tokens (if any) to transfer
- Data – arbitrary payload used to invoke contract functions
- Gas Limit (StartGas) – maximum computational effort permitted
- Blob References (optional) – references to blob data, for rollup use cases
- GasPrice – always set to 0 at the user level, as gas is abstracted away by the protocol •
- Chain ID and Nonce – used for replay protection and uniqueness
Unlike Ethereum, the user pays no fees. Gas costs are internally managed using the GAS token, a non-tradable technical token minted per block and allocated to users as needed. From a user perspective, transactions are free, while internally, the EVM still meters and tracks gas for consistency and resource control.
Blob Transactions (EIP-4844)
With Dencun integration, LibraChain supports blob-carrying transactions introduced in EIP-4844 (Proto-Danksharding) . These enable temporary, low- cost storage of large data payloads — ideal for rollups and L2s.
Key attributes of blob tx:
- Blobs are stored in a data gas market separate from base calldata
- Each blob has a ~18-day lifetime (4096 epochs)
- Contracts can reference blobs for data but cannot directly read them from the execution layer
This significantly reduces rollup data costs and improves scalability.
A message is an internal call between contracts, never serialized or sent over the network. It includes:
- Sender – the contract that created the message
- Recipient – the contract receiving the message
- Value – LIB token transfer amount
- Data – function arguments or payload
- Gas allocation – a portion of the parent’s remaining gas
Messages are created when a contract uses the{" "} {" "} CALL, DELEGATECALL, STATICCALL , or CREATE opcode.
Just like transactions, message calls in LibraChain benefit from:
- Gasless abstraction (from the user’s perspective)
- Full EVM compatibility
- Reduced calldata costs if using blob references
Execution Tree Example
If EOA Alice sends a transaction with a 100,000 gas limit to Contract A, and A uses 40,000 gas before calling Contract B with 30,000 gas, then:
- Contract B may use 30,000 gas
- If it returns successfully, Contract A resumes with 30,000 gas remaining
- If B fails or runs out of gas, Contract A’s call will revert
All of this is internally covered by the GAS allocation — the user (Alice) pays nothing.
Summary
LibraChain maintains full EVM support while improving the transaction and contract interaction model through:
- Gas abstraction with dynamic internal GAS allocation
- Native support for blob transactions under EIP-4844
- Lower calldata and rollup data costs
- Transparent and fee-less experience for users and Dapps
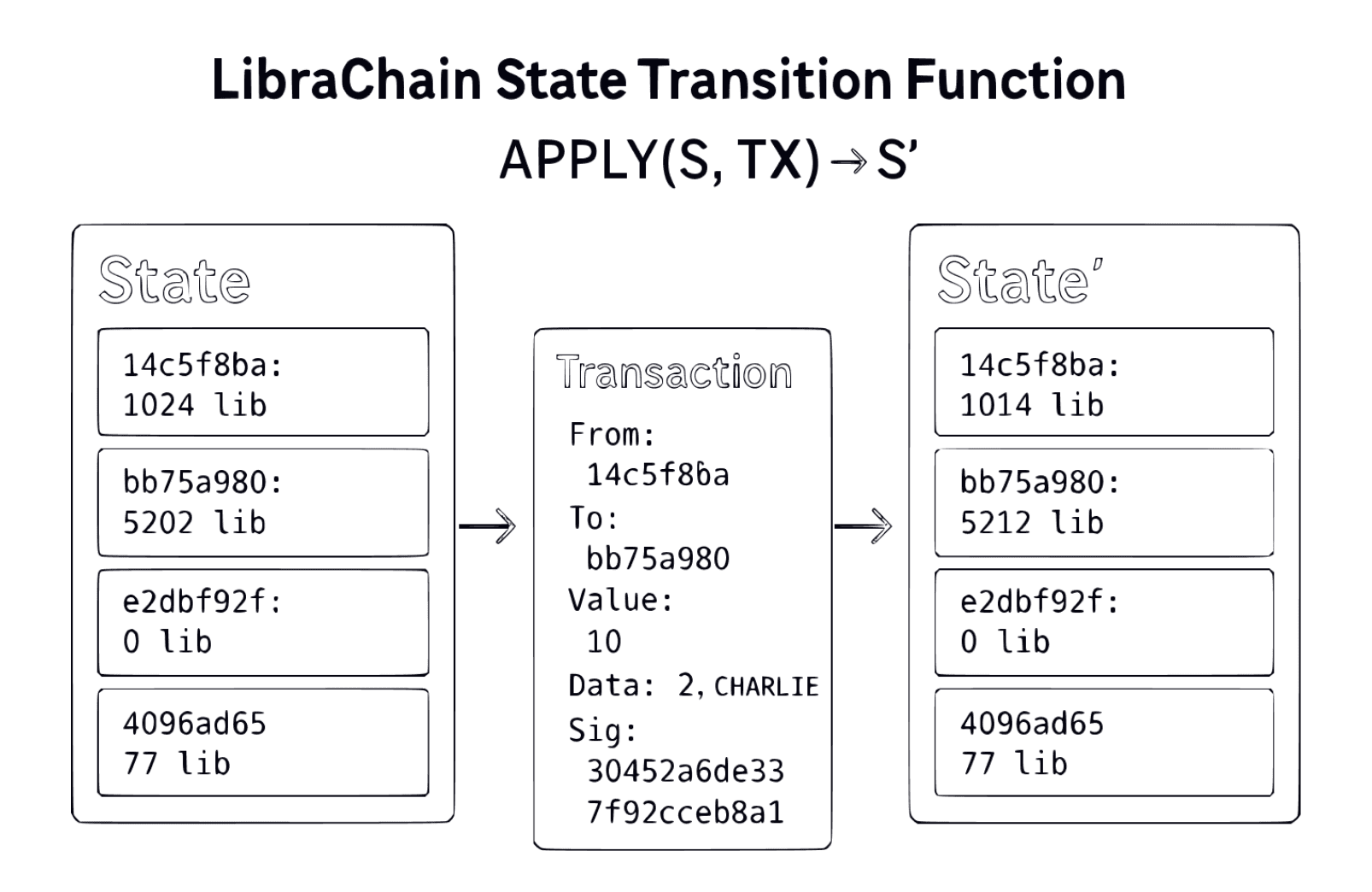
State Transition Function — APPLY(S, TX) → S′
Preliminaries
Account model matches Ethereum (EOAs & contracts). Consensus is Proof of
Stake (Prysm client). EVM gas metering is preserved, but end‑users never pay
fees: gas is covered by an internal, non‑tradable GAS token minted per block
and allocated dynamically. Dencun (EIP‑4844) blob‑carrying transactions are
supported with a separate data‑gas market; blobs are retained for ~18 days.
Transaction fields (execution‑relevant)
to (recipient; absent ⇒ contract creation); value (LIB); data (call data /
init code); nonce; gasLimit; signature; optional blobVersionedHashes[] with
data‑gas variables; EIP‑1559 fields are accepted for compatibility but
effective user gas price is 0 on LibraChain.
Algorithm (LibraChain)
- 1) Verify structure, chain ID, and signature; recover sender. If invalid, reject.
- 2) Check nonce equality; if mismatch, reject.
- 3) Compute intrinsic gas; validate blob commitments and data‑gas limits if present; require gasLimit ≥ intrinsic.
- 4) Allocate internal GAS sponsorship: gasRemaining := gasLimit; increment sender.nonce (anti‑replay).
- 5) If value {">"} 0, require sender.balance ≥ value; debit/credit balances; create recipient if needed.
- 6) Execute EVM (or init code on creation) with gasRemaining; child calls/messages receive slices of remaining gas.
- 7) If OOG/REVERT: revert execution state; nonce stays incremented; keep internal gas accounting.
- 8) If success: commit execution state; unused internal GAS is released back to the protocol pool (no user refund).
- 9) Finalize: record gasUsed and blobGasUsed in receipt; update per‑block accounting for LIB validator rewards; emit logs/bloom; return S ′.
Safety property
As in Ethereum, if A calls B with G gas, A can lose at most G gas. Child
reverts revert their own sub‑state unless bubbled up; parent execution need
not revert.
Worked example (gasless)
Tx: value=10 LIB, gasLimit=2000, data=64 bytes, no blobs. Validate
sig/nonce; allocate internal GAS; transfer 10 LIB to contract; contract
writes storage slot[2] = CHARLIE using 187 gas; commit state; user pays 0;
gasUsed recorded for validator LIB rewards; no user refund step exists.
Dencun / blobs note
For blob‑carrying txs: validate versioned hashes, account data‑gas in the
blob market, respect block data‑gas limits; blobs are stored off‑EL with
~18‑day retention; contracts reference them but cannot read bytes directly
from EL.
Figure: LibraChain APPLY(S, TX) → S′ with Internal GAS Sponsorship and EIP‑4844 Data‑Gas (diagram placeholder)
Code Execution in LibraChain
The code in LibraChain smart contracts is written in Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) bytecode — a low-level, stack-based instruction set inherited from Ethereum. LibraChain preserves full EVM compatibility , ensuring that contracts developed for Ethereum or other EVM-based chains execute identically.
A contract’s code is a series of bytes, where each byte corresponds to an opcode . Code execution generally follows an instruction fetch–execute cycle :
- Program Counter (PC) starts at zero.
- The opcode at the current PC is fetched.
- The corresponding operation is executed
- The PC is incremented (or modified by control flow instructions such as JUMP).
- Execution repeats until a STOP, RETURN, REVERT , or error condition is encountered.
Execution Data Spaces
Contracts have access to three distinct storage areas during execution
- Stack – A last-in, first-out (LIFO) container for 256-bit words. Used for intermediate values. All arithmetic and logical operations interact with the stack
- Memory – A byte-addressable, infinitely expandable array used for temporary data. Reset after execution ends.
- Storage – A persistent key–value store associated with the contract account. Unlike stack and memory, storage persists between executions and is part of the blockchain state.
Additional Accessible Context
During execution, contracts can access:
- Message context – msg.sender, msg.value, msg.data, and msg.gas (tracked internally for metering but not billed to the user in LibraChain)
- Blockchain context – block number, timestamp, base fee, blob commitments (from EIP-4844), and other header fields
- Return data – contracts can return byte arrays as output
Execution Model in LibraChain (Gasless Context)
In Ethereum, execution consumes gas charged to the sender at a GASPRICE. In LibraChain
- EVM gas metering remains fully functional for determinism and consensus consistency.
- End-users pay no fees . Gas is covered by the internal GAS token , allocated from a per-block protocol budget.
- All gas usage is tracked and attributed internally for validator LIB rewards.
- Contracts still face out-of-gas halts to prevent denial-of-service and infinite loops
Dencun Upgrade Impacts on Execution
LibraChain integrates all execution-layer improvements from Ethereum’s Cancun fork:
- EIP-1153 (Transient Storage) – enables temporary storage locations that clear automatically at the end of execution
- EIP-5656 (MCOPY) – optimized memory copying
- EIP-4844 (Blob Transactions) – execution context can reference blob commitments and metadata for rollup/L2 interactions, though blob data itself is not directly accessible from the EVM.
- Gas metering for blobs – recorded separately as data gas , not mixed with execution gas.
Formal Execution State
At any point, the EVM’s full computational state in LibraChain can be
represented by:
block_state, transaction, message, code, memory, stack, pc, gas)
Where:
- block_state – complete global blockchain state (accounts, balances, storage, code)
- transaction – current transaction being processed
- message – current call frame’s context (sender, value, data)
- code – bytecode of the executing contract
- memory – volatile temporary data storage
- stack – LIFO stack for intermediate values
- pc – program counter
- gas – remaining gas (tracked internally, decremented per operation)
Example Operations
- ADD – Pops the top two stack items, pushes their sum, decrements gas by 3 (as per EVM rules), increments pc by 1.
- SSTORE – Pops two stack items, stores the second in storage at the slot index given by the first, adjusts gas according to storage rules (e.g., cold/warm slot access).
- MCOPY – Copies a range of bytes in memory to another location, optimized in EIP-5656.
Implementation Notes
While highly optimized JIT compilers and EVM interpreters exist, a basic EVM implementation can be achieved in a few hundred lines of code. LibraChain’s execution layer can integrate the same optimizations as Ethereum clients while preserving gasless semantics at the protocol level.
Block Validation and Architecture in LibraChain
The LibraChain blockchain shares many architectural similarities with Ethereum, but incorporates several key differences aligned with its gasless transaction model, Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus, and Dencun upgrade enhancements.
Key Differences from Ethereum
- Consensus Layer – LibraChain uses PoS with Prysm Beacon Chain for validator coordination, replacing Ethereum’s Proof-of-Work (PoW) entirely. Block production and finality are driven by validator attestations rather than mining difficulty.
- Gasless Transactions – While the EVM still meters gas internally for execution determinism, transaction fees are covered by the protocol using the internal GAS token, meaning end-users incur no direct fees.
- Dencun Features – Full support for EIP-4844 blob transactions, transient storage (EIP-1153) , and MCOPY (EIP-5656) is integrated at the execution level. Blob data enables efficient rollup scaling with lower calldata costs.
- State Commitment Optimizations – LibraChain retains Ethereum’s Merkle Patricia Tree model for state storage but implements optimized node storage for faster syncing and reduced disk usage.
Block Structure
Each LibraChain block contains:
- Block Header – includes block number, slot, parent hash, state root, transaction root, blob commitments root, and validator signatures.
- Transaction List – the ordered list of transactions included in the block.
- Finalized State Commitment – the state of all accounts and storage after processing all included transactions.
Unlike Bitcoin, where blocks store only transactions, LibraChain (like Ethereum) stores both the transactions and the post-state root.
Block Validation Algorithm in LibraChain
The block validation process, adapted for LibraChain’s PoS and gasless model, is as follows:
-
Parent Block Validation
- Verify the parent block exists and is valid
- Confirm the slot/epoch sequencing is correct.
-
Timestamp & Consensus Checks
- Ensure the block timestamp is greater than its parent’s and within the allowable drift defined by the consensus protocol
- Validate the block proposer’s eligibility and BLS signature against the Beacon Chain validator set
-
Header Field Verification
- Validate block number, blob commitments root, transaction root, and state root.
- Check that the gas limit and gas used are within protocol-defined bounds.
-
State Transition Execution
- Let S[0] be the state at the end of the parent block
- Let TX be the list of transactions
- For each transaction TX[i], apply APPLY(S[i], TX[i]) to obtain S[i+1]
- If any transaction execution fails due to invalid signature, insufficient balance for value transfer, or exceeding the per-transaction gas limit, revert that transaction but continue processing the rest of the block.
- Track gas usage for validator rewards internally, even though users are not charged
-
Protocol Rewards
- Let S_FINAL = S[n], then distribute the validator reward in LIB to the block proposer and attesters.
- GAS token allocations for covering execution costs are minted per protocol rules
-
State Root Verification
- Compute the Merkle Patricia Tree root of S_FINAL
- If it matches the stateRoot in the block header, the block is valid; otherwise, reject it.
State Storage Model
LibraChain uses Ethereum’s modified Merkle Patricia Tree (MPT) to store account and contract state.
- Only a small subset of the tree changes from block to block, so most of the state data is referenced via shared subtree hashes.
- Blob transactions store large data payloads off-chain but commit proofs in the block header, reducing calldata footprint.
- This structure allows nodes to prune historical state and maintain only the latest snapshot plus minimal proof data, significantly reducing storage requirements.
Code Execution Location
Contract code execution is performed during block validation by every validator node . If a transaction is included in block B, the contract execution it triggers will be re- executed by all nodes that download and validate block B, both now and in the future. This ensures deterministic consensus across the network
4. Applications
LibraChain is designed as a next-generation execution layer for decentralized applications (DApps), with a focus on removing the onboarding and usability friction that has historically limited mainstream adoption of blockchain technology.
In traditional EVM-based environments, users must hold native tokens to pay transaction fees, navigate complex wallet setup processes, and manage gas price selection. LibraChain eliminates these barriers through its gasless transaction model , powered by the internal GAS token. This approach allows end-users to interact with DApps without ever holding LIB or any other cryptocurrency, while still maintaining EVM compatibility and execution determinism
Key Advantages for Developers and Users
-
Frictionless Onboarding
- New users can interact with DApps instantly using familiar sign-in methods (e.g., email, social login, or custodial wallet solutions).
- No prior wallet setup or LIB token acquisition is required — the protocol transparently covers gas costs
-
Dencun Upgrade Capabilities
- Support for EIP-4844 blob transactions allows cost-efficient data availability for rollup-based applications, such as high-volume gaming, social networks, and enterprise blockchains.
- Reduced calldata costs lower operational expenses for developers, enabling microtransactions and data-heavy use cases that were previously uneconomical.
-
Mainstream UX for Web3
- Users experience blockchain interactions with the same simplicity as Web2 applications, while benefiting from self-custody and decentralization when desired.
- Developers can design DApps without the need to educate users about gas mechanics.
-
Enterprise Integration
- Gasless architecture and predictable execution costs make LibraChain suitable for enterprise workflows, where operational budgeting and user simplicity are critical.
- Businesses can sponsor user interactions without exposing them to crypto volatility.
Potential Application Domains
- Gaming & Metaverse – Low-latency, microtransaction-heavy environments where users may not even realize blockchain technology is being used.
- Social Media & Content Platforms – Decentralized content posting, tipping, and creator monetization without friction from gas fees.
- DeFi Protocols – Yield farming, staking, and trading where onboarding is seamless for new users without pre-funded wallets.
- Enterprise and Government Services – Identity verification, notarization, and supply chain tracking, all accessible via gasless end-user interactions.
- Rollup & L2 Ecosystem – Leveraging blob transactions for scalable rollup data publishing.
Developer Benefits
LibraChain’s EVM compatibility means existing Ethereum smart contracts can be deployed with minimal changes. Developers gain access to:
- Gasless APIs for sponsored transactions.
- Enhanced state storage efficiency for high-throughput applications.
- Blob storage capabilities for off-chain data commitments.
By combining zero gas onboarding, EIP-4844 scalability , and full EVM compatibility , LibraChain provides a unique execution environment optimized for the next billion blockchain users
5. Token Model
LibraChain operates on a dual-token architecture designed to optimize both network efficiency and ecosystem value creation :
-
GAS – Technical &
Operational Token
- Purpose : Serves exclusively as the network’s internal mechanism for transaction execution.
- Value : Zero monetary value; not tradable on exchanges.
- Supply : Infinite; minted dynamically per block based on network usage.
- Function : Abstracts away gas costs from end-users by automatically refilling transaction execution balances, ensuring a seamless, “gasless” experience.
-
LIB – Governance &
Utility Toke
- Purpose : The primary economic driver of the LibraChain ecosystem.
- Tradability : Fully tradable on exchanges
-
Utility:
- Staking to secure the network and participate in validator operations.
- Earning validator and delegator rewards.
- Funding ecosystem growth through incentives, grants, and liquidity programs.
- Participating in on-chain governance to shape protocol upgrades and strategic decisions.
This model ensures technical scalability through GAS while enabling economic sustainability and community empowerment through LIB.
6. Consensus and Governance
Consensus Mechanism — Proof of Stake (PoS) via Prysm Beacon Chain LibraChain employs a Proof of Stake consensus protocol powered by the Prysm Beacon Chain , ensuring high throughput, energy efficiency, and rapid finality. Validators are responsible for proposing and attesting to blocks, securing the network through stake-based economic incentives. Finality is achieved within seconds, minimizing the risk of chain reorganizations and providing a robust security framework suitable for enterprise-grade and consumer-facing applications.
Validator onboarding is streamlined through one-click setup , removing the technical barriers that traditionally hinder participation. The network’s mesh technology further enhances decentralization by enabling efficient peer-to-peer propagation of blocks and attestations, optimizing performance even at scale
Governance — LIB Token Holder Voting
LibraChain implements an
on-chain governance system
that empowers LIB token holders to actively shape the future of the
protocol. Governance proposals may include:
- Protocol Upgrades — such as consensus improvements, gas abstraction enhancements, or EVM optimizations
- Economic Parameters — including validator rewards, staking requirements, and ecosystem fund allocation.
- Interoperability Expansions — enabling new cross-chain bridges, standards, and integrations
Voting power is proportional to the amount of LIB staked, aligning the decision- making process with stakeholders’ vested interest in the long-term security and growth of the network. Governance execution is transparent, verifiable on-chain, and finalized through smart contract–enforced rules to prevent arbitrary changes.
Core Principles of LibraChain Governance
- Decentralized Decision-Making — No single entity can unilaterally alter core protocol rules.
- Security-First Policy — All proposed upgrades undergo multi-stage review, including community testing on public testnets.
- Interoperability-Focused Evolution — Governance prioritizes initiatives that enhance LibraChain’s role in a multi-chain Web3 ecosystem.
7. Technical Chain Specs
Base Architecture — Ethereum Dencun (Deneb) Fork LibraChain is built as a Layer 1 blockchain forked from Ethereum’s Dencun (Deneb) upgrade , inheriting the latest protocol optimizations including EIP-4844 proto-danksharding , blob transactions, and reduced calldata costs. This foundation ensures native compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and seamless deployment of existing Ethereum-based smart contracts.
Block Time & Finality
- Average Block Time : ~6 seconds, enabling high transaction throughput and low confirmation latency.
- Fast Finality : Achieved through Proof of Stake with Prysm Beacon Chain, reducing the risk of chain reorganizations and providing near-instant settlement guarantees for both users and dApps.
Gas Scaling & Throughput
LibraChain implements
adaptive block gas limit scaling
that dynamically increases by up to 10% under network load. This allows:
- Up to 500 ERC-20 transfers per block under normal conditions.
- Execution of complex transactions consuming up to ~250,000 gas. This scalability model ensures the network remains performant during demand spikes without compromising stability.
Mesh Networking Technology
LibraChain integrates a mesh-based peer-to-peer propagation layer
that enhances scalability, resilience, and redundancy. Mesh networking
enables faster block and attestation dissemination across geographically
distributed validators, ensuring high network efficiency and uptime even
under adverse conditions.
Key Technical Advantages
- Gasless User Experience : Enabled via automated GAS token refills
- EVM Compatibility : Full support for Solidity and Vyper smart contracts.
- Optimized Data Availability : Through Dencun’s blob transaction model.
8. Validator Design
One-Click Validator Onboarding
LibraChain is engineered for
rapid validator participation
through a
one-click setup process
available via both
GUI
and
API . This dramatically
lowers technical barriers, enabling individuals, institutions, and staking
services to join the network without deep protocol knowledge or complex
infrastructure setup
Proof of Stake via LIB Token
Validators secure the network by staking
LIB , the native
governance and utility token of LibraChain. Staking aligns incentives
between network participants and the protocol, ensuring validators are
economically invested in maintaining consensus integrity and uptime.
Rewards and Penalties
- Rewards : Validators receive LIB token rewards for proposing and attesting blocks, proportional to their stake and performance.
- Slashing : Inactive or malicious behavior is deterred through slashing conditions that follow Ethereum’s Beacon Chain standards This ensures network security while maintaining validator accountability.
Integration with Mesh Technology
Validator nodes benefit from LibraChain’s
mesh networking layer
, improving block propagation speeds and reducing the risk of missed
attestations due to latency or network congestion.
9. Tokenomics (Total Supply: 250m LIB)
- Ecosystem Growth – 25% (Cliff 6m, Vesting 36m
- Foundation Reserve – 20% (Cliff 12m, Vesting 48m)
- Investors (Seed + VC) – 15% (Cliff 6m, Vesting 24m)
- Team & Advisors – 15% (Cliff 12m, Vesting 36m)
- Liquidity & MM – 10% (Cliff 0m, Vesting 12m)
- Public Sale – 10% (Cliff 0m, Vesting 0m)
- Airdrop & Community – 5% (Cliff 0m, Vesting 6m)
10. Team
- Suren Alaverdyan – Founding Member & CIO
- David Vardanyan – Founding Member & CEO
- Freedx Team – Provided over 90 resources, including strategic leadership and financial support.
11. Future Directions
In the long term, LibraChain aims to serve as the foundational infrastructure for a global, permissionless digital economy where the barriers between traditional applications and decentralized protocols disappear. By abstracting gas costs through its internal GAS mechanism, and enabling scalable, cost-efficient data publishing via Dencun’s blob transactions , LibraChain creates an environment where developers and enterprises can deploy decentralized services with Web2-level usability but Web3-grade trust guarantees .
The network’s Proof-of-Stake consensus ensures sustainable security and fast finality, while its EVM compatibility guarantees a seamless migration path for the vast ecosystem of existing Ethereum applications. As adoption grows, LibraChain envisions becoming the default execution layer for a new class of applications that are invisible in complexity but powerful in capability — from frictionless micropayments and decentralized identity systems to high-frequency gaming and global-scale data marketplaces
In this future, users interact with blockchain applications without ever thinking about gas, wallet setup, or crypto volatility , while developers tap into a global, interoperable, and enterprise-ready infrastructure that makes the decentralized internet a practical reality for billions
One of the key plans of LibraChain is interoperability
12. Conclusion
LibraChain redefines the Layer 1 blockchain experience by delivering gasless transactions, frictionless validator onboarding , and a foundation for sustainable ecosystem growth . Built as a fork of Ethereum’s latest Dencun upgrade , it combines the proven security and decentralization of Ethereum with innovations in gas abstraction, mesh networking, and adaptive scaling
By prioritizing user experience, developer accessibility , and interoperability , LibraChain is positioned to serve as the next-generation platform for Web3 adoption —removing barriers, empowering creators, and enabling seamless integration into the global digital economy.